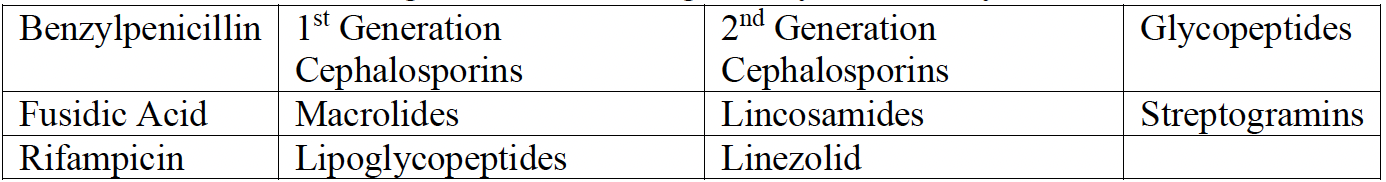
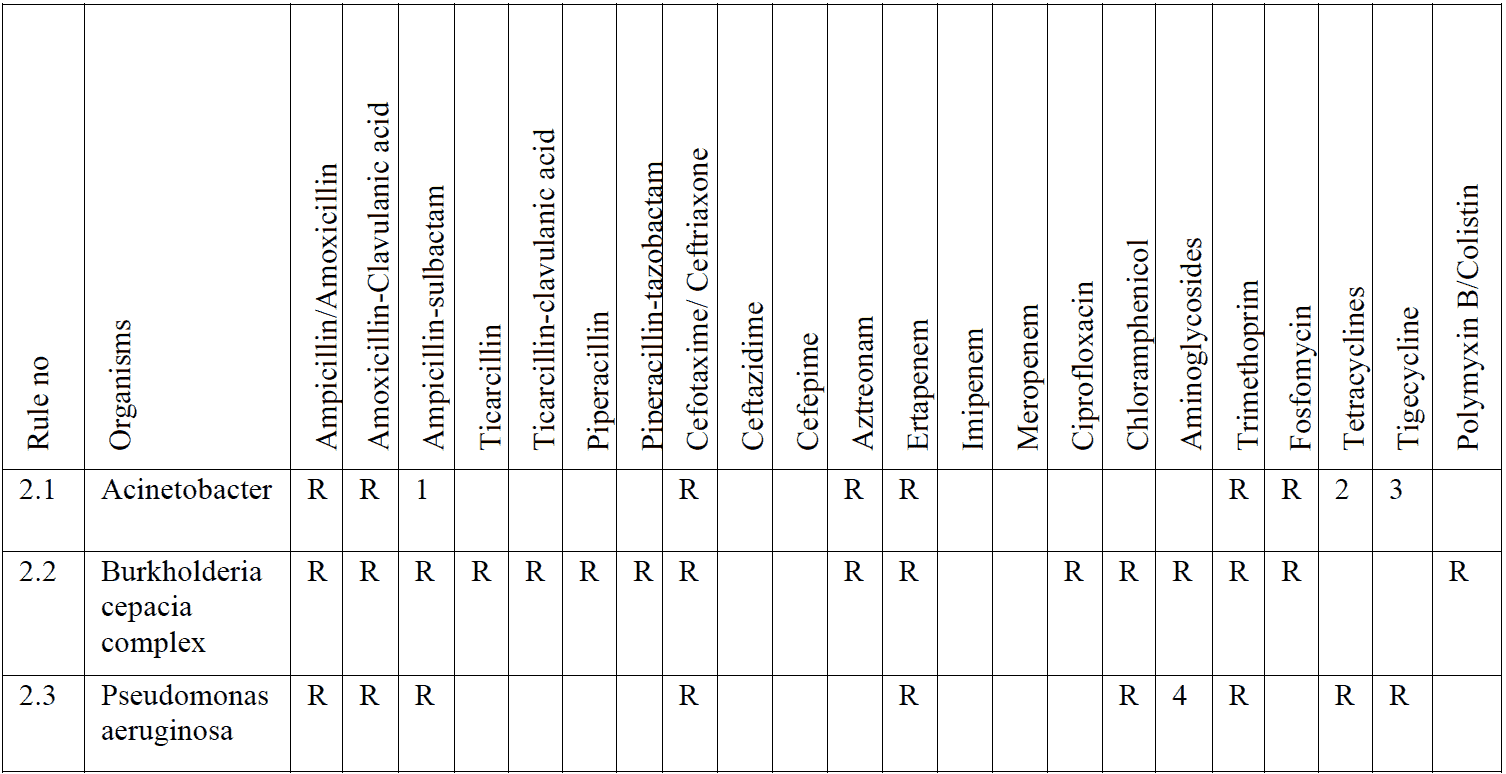
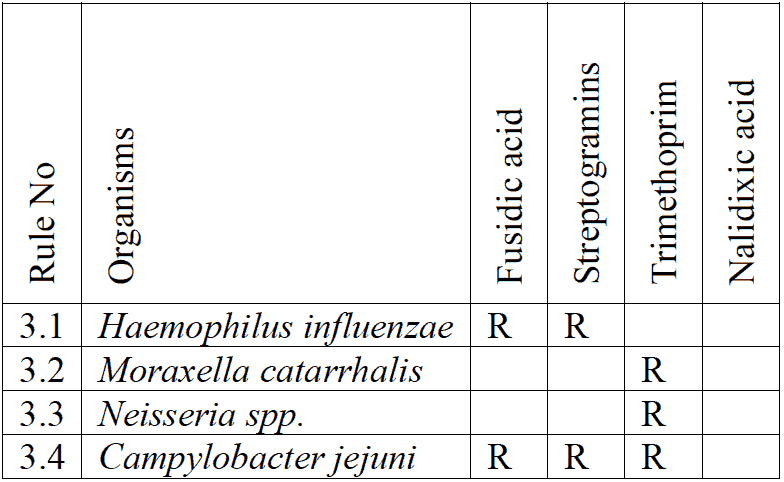
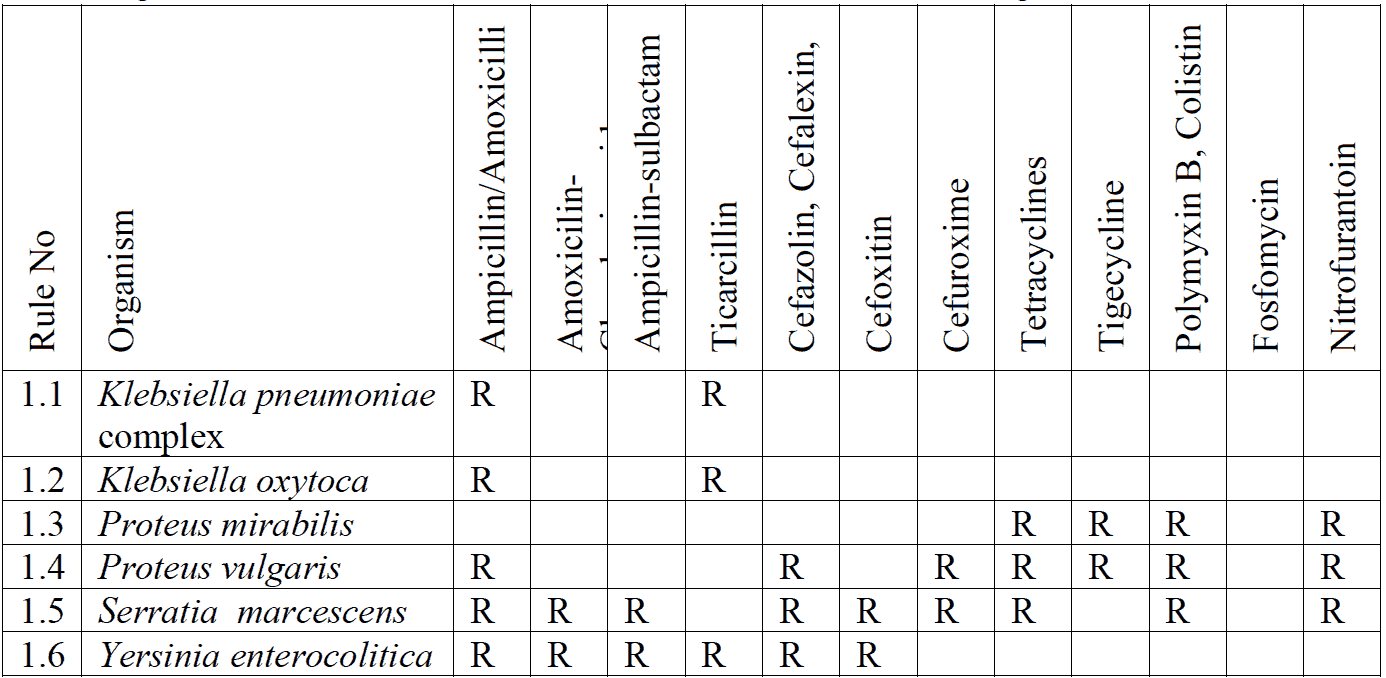
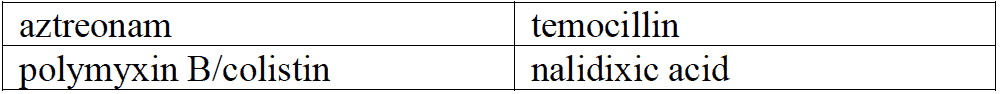Enterobacterales are intrinsically resistant to-

Following members of Enterobacterales are also resistant to following antibiotics:
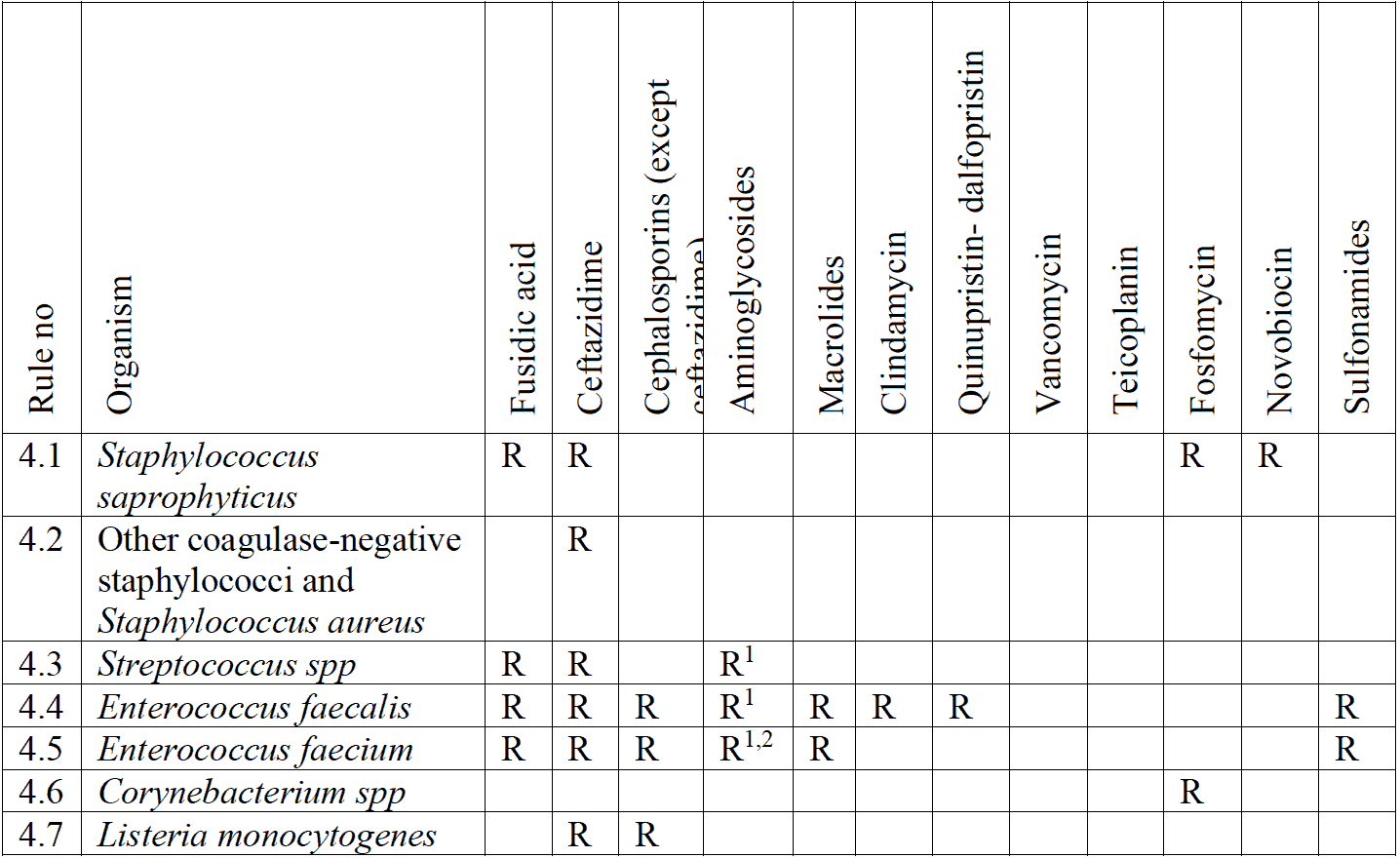
R = Resiatant
1. Azithromycin is effective in vivo for the treatment of typhoid fever and erythromycin may be used to treat travellers’ diarrhea.
2. For Salmonella spp and Shigella spp aminoglycoside, 1st and 2nd Generation Cephalosporines and Cephamycines may appear active in vitro but not effective clinically and should not report as susceptible.