6. Diagnosis of Human Rabies
exp date isn't null, but text field is
6.1 Laboratory Procedures
- Identification and confirming suspected cases by clinical and laboratory investigation is essential for rabies surveillance and elimination.
- For laboratory diagnosis, recommended samples are saliva, skin (frozen section of nuchal skin biopsy material), tissues, brain, blood/ serum.
- Samples to be collected by trained clinicians or medical technologists, to be preserved in Glycerol (GS)/normal saline and transported in a cool box with 4 ice packs to the laboratory and to be stored in -20ºC to-80ºC temperature.
- Samples to be tested in BSL2 laboratory (Human health laboratory) by trained and skilled laboratory personnel.
The rabies virus can be detected in the lab by any of the following procedures such as,
- Antigen detection: There are two types of tests practiced-
FAT: Immunofluorescence microscopy can detect Rabies Ag in acetone fixed tissue incubated at 37ºC.
DRIT: Normal microscopy Immunohistochemistry method can detect rabies virus inclusions in formalin-fixed tissues, incubation at room temperature.
- Virus detection: RT-PCR or cell culture from saliva, skin, corneal wash sample.
- Antibody detection: From serum by Rapid Fluorescent Focus Inhibition Test (RFFIT) procedure (neutralization test), ELISA.
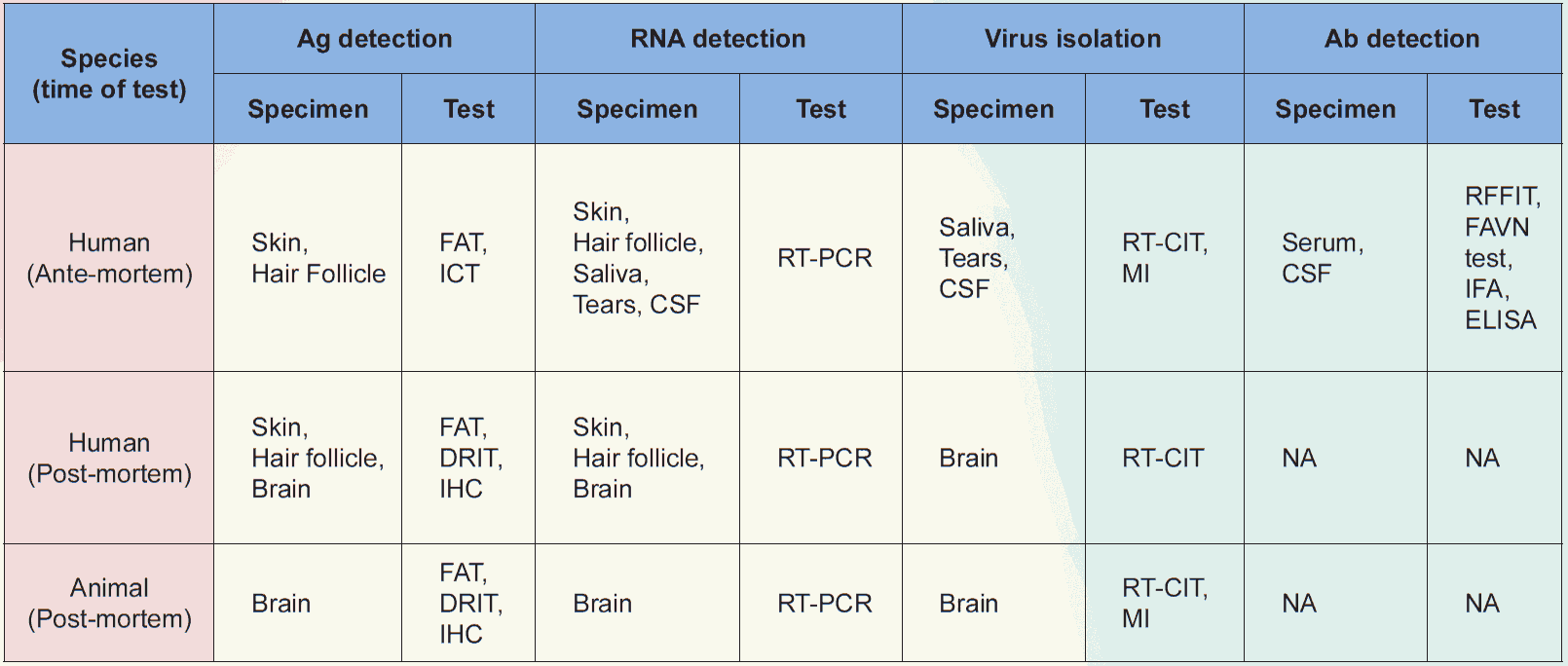
Table 7: Standard Diagnostic Test for Rabies Virus (Annex 2)1