2.2 Diagnosis of prediabetes and diabetes
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Diagnosis is based on documentation of glucose intolerance in an individual. Procedures for documenting glucose intolerance include:
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) – gold standard test
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG)
- HbA1c (Glycated hemoglobin)
- Random plasma glucose (RPG)
2.2.1 OGTT (gold standard test)
Plasma glucose level is determined at fasting and 2 hours after 75 grams (1.75-gram glucose/kg body weight, up to maximum 75-gram glucose for children) of oral glucose drink. It classifies a person as a diabetic, IGT (impaired glucose tolerance), IFG (impaired fasting glucose) or normal.1,5
OGTT procedure5
- Person should take unrestricted diet containing at least 150 grams of carbohydrate daily for at least previous 3 days.
- The test should be done in the morning after 8-14 hours of overnight fast (Preferably before 9 am).
- A fasting blood sample prior to glucose drink is collected.
- An oral glucose load of 75-gram of anhydrous glucose for adult (1.75-gram glucose/kg body weight, up to maximum 75-gram glucose for children) is given in 250-300 ml of water. The drink must be completed within 5 minutes.
- A second blood sample is collected at 120th minute after the glucose drink.
- If glucose is not estimated immediately then the blood sample may be preserved with sodium fluoride (6 mg/ml whole blood), blood should be centrifuged, and plasma separated and frozen until estimation.
- Smoking, tea or physical stress is not allowed during the test.
2.2.2 FPG
By fasting plasma glucose level, a person can be labeled as a diabetic, but cannot exclude diabetes.1,5
2.2.3 HbA1c
HbA1c is now increasingly being used in diagnosis of diabetes. The test must be highly standardized for using it in this purpose.1,5
2.2.4 RPG
No preparation is required for this procedure. Plasma glucose levels are estimated from a sample irrespective of last meal. RPG, in presence of classical symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis can confirm diabetes.1
Table 2.1 Diagnostic criteria for prediabetes (IFG and IGT) and diabetes mellitus for nonpregnant adults and children1,5
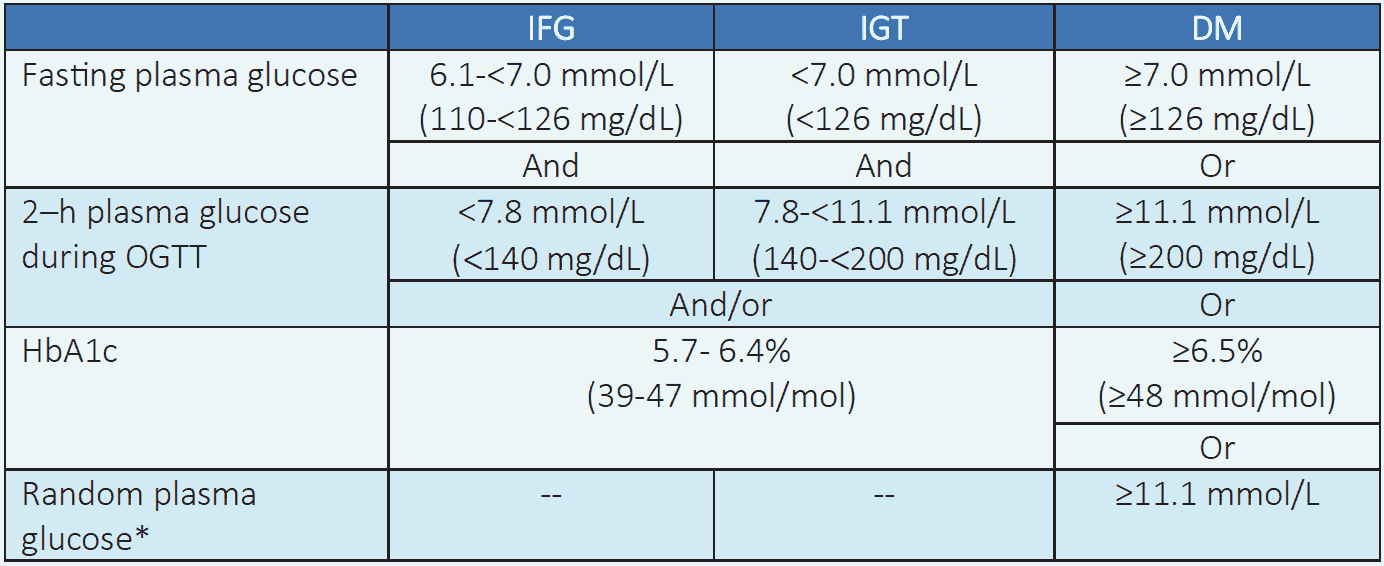
NB: *In presence of classical symptoms of hyperglycemia (polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weight loss and generalized weakness) or hyperglycemic crisis.
Table 2.2 Diagnostic criteria for hyperglycemia in pregnancy6

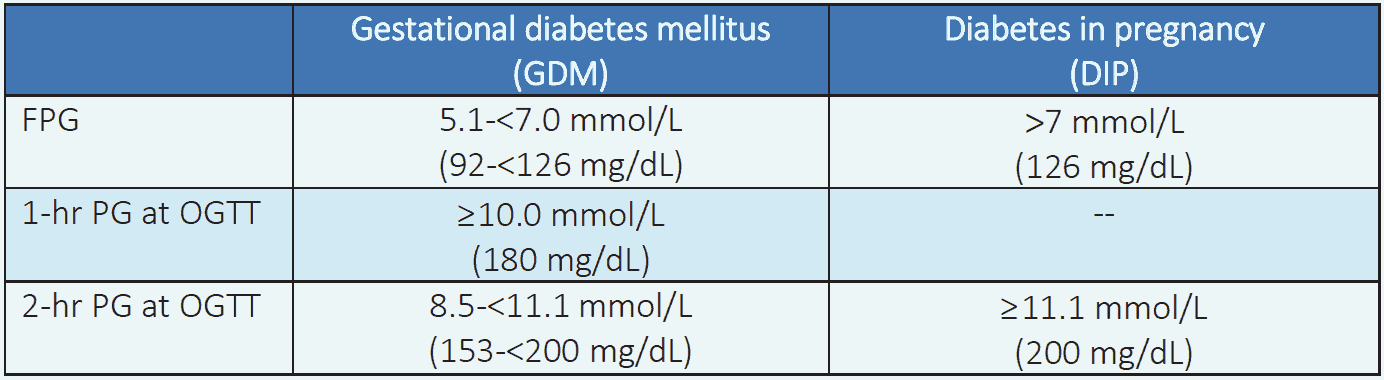
NB: Diagnosis is made when any one of the plasma glucose values is met. Performed with a 3-step 75-gm OGTT at any time in pregnancy. All values are venous plasma glucose.
