Executive Summary
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Executive summary
- Comprehensive medical assessment is imperative for people with DM.
- In the management of diabetes diet and exercise are mandatory for all individuals.
- Insulin is the only pharmacotherapy for T1DM on the other hand various classes of medications including sulfonylureas, meglitinides (non-sulfonylureas), biguanides, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP1) receptor agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors, sodium glucose cotransporter- 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors and insulin can be used in T2DM.
- The presence of complications or comorbidities such as ASCVD, CKD, and heart failure also has an important role in determining therapy.
- Monitoring of glycemic control by SMBG and CGM are important components of diabetes management.
Treatment of DM is always individualized. T1DM always requires insulin but the management of T2DM is of great challenge and require appropriate decision making. Not only the glycemic control but CVD risk, presence of comorbidities and complications need to be considered when choosing a particular antidiabetic agent.
Table 3.1 Factors to be considered before selection of antidiabetic agent1,2
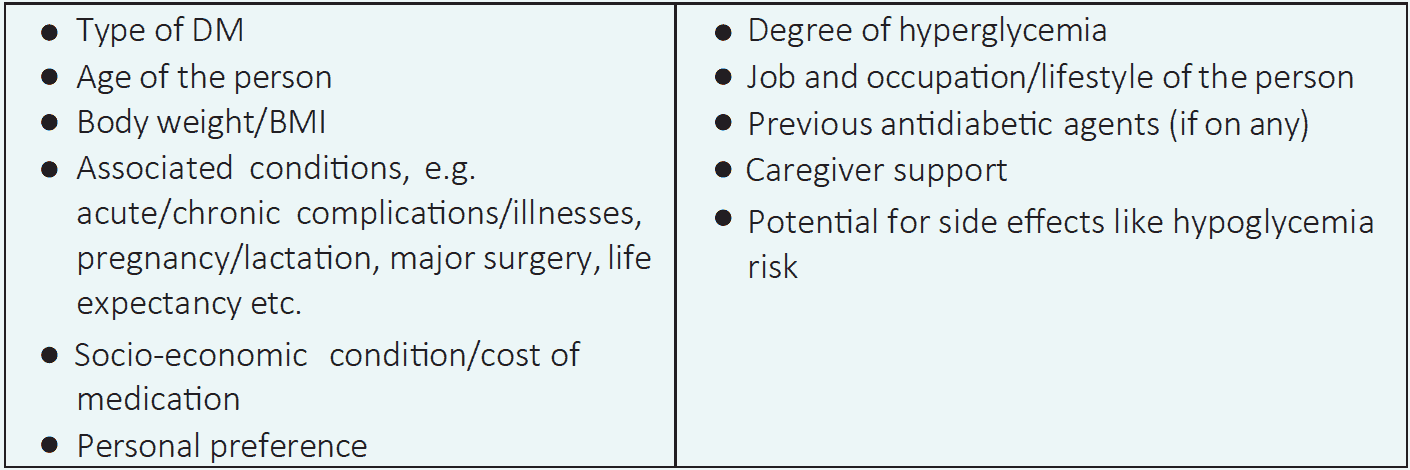
Table 3.2 Target of diabetes management (in non-pregnant adult)2
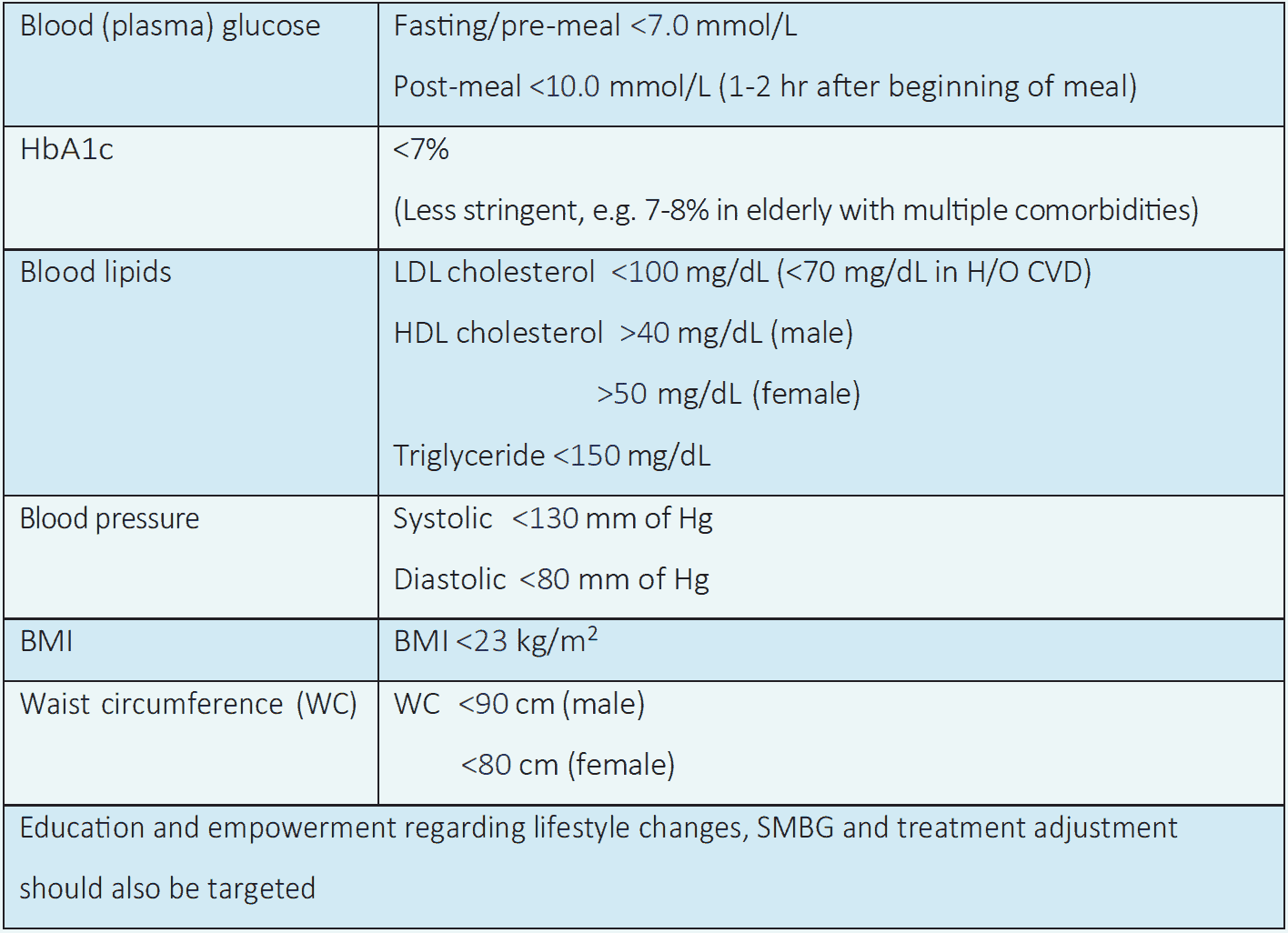
NB: Target of glycemic control may be individualized considering individual factors.
