6.2 Secondary Hypertension
exp date isn't null, but text field is
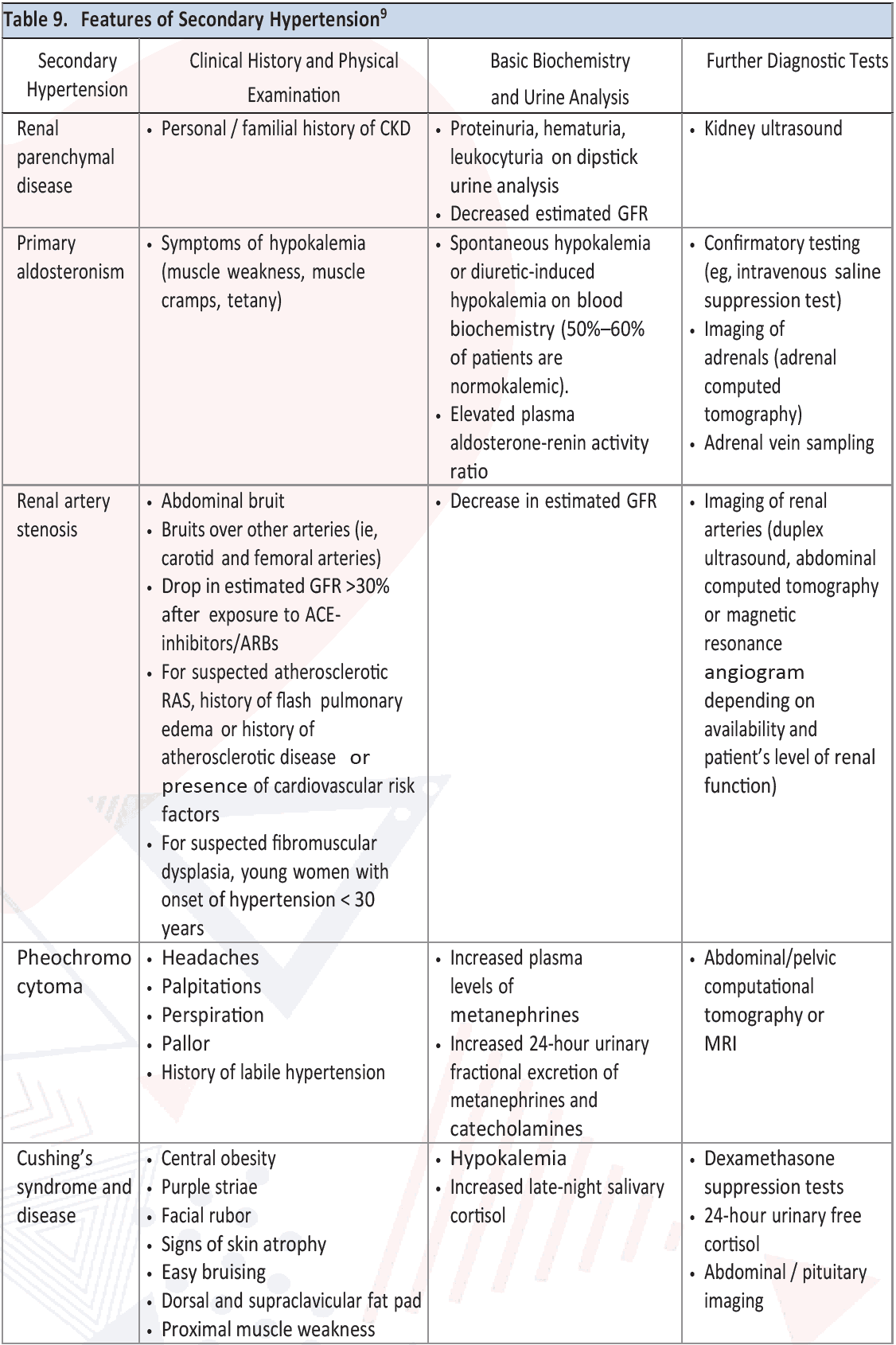
Secondary hypertension is a type of hypertension which results from an identifiable underlying cause. It affects only 5% to 10% of hypertensive patients. The most common types of secondary hypertension in adults are renal parenchymal diseases, renovascular hypertension, primary aldosteronism, chronic sleep apnea, and substance/drug induced. Secondary causes of hypertension and their features are given in Table 9.
Additional investigations of patients for secondary causes of hypertension are particularly appropriate in the following groups:
- Patients with early onset hypertension under 30 years of age in particular in the absence of hypertension risk factors
- Patients with hypertension urgency or emergency
- Patients resistant to antihypertensive therapy
- Patients with abnormal renal function, proteinuria, or hematuria
- Patients with hypokalemia without diuretic therapy
- BP begins to increase for uncertain reasons after being well controlled.
- Onset of hypertension is sudden.
Treatment of secondary hypertension depends on the causes of high blood pressure.