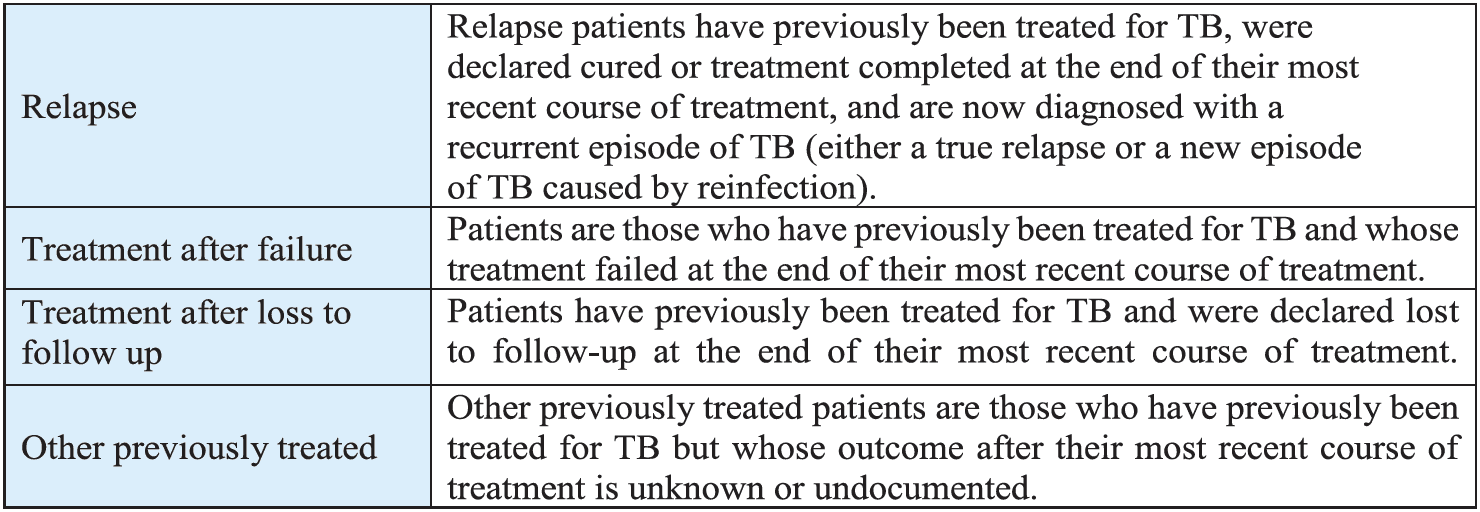
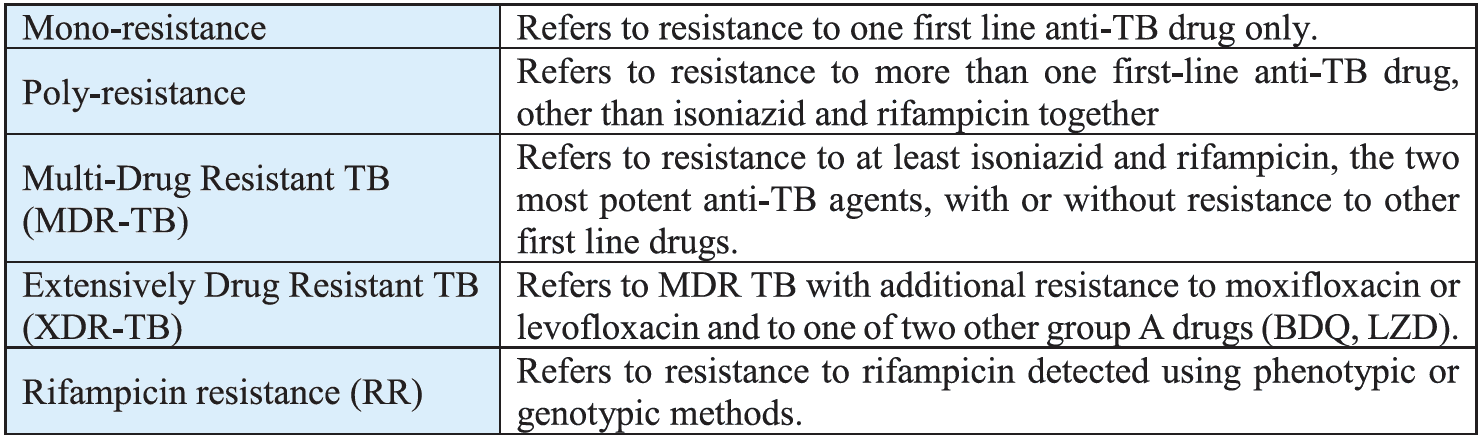
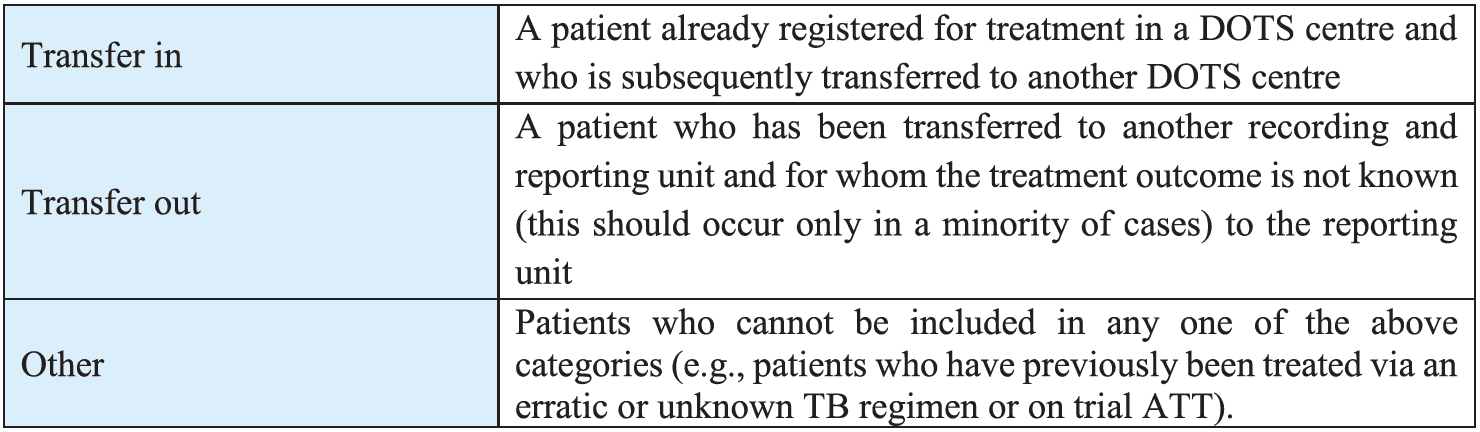
The TB Cases are categorised in to Pulmonary and Extra Pulmonary TB based on the anatomical site of the disease.
Pulmonary TB (PTB)
Pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) refers to any bacteriologically confirmed or clinically diagnosed case of TB involving the lung parenchyma or the tracheobronchial tree. Miliary TB is classified as PTB because there are lesions in the lungs. Tuberculous intra-thoracic lymphadenopathy (mediastinal and/or hilar) or tuberculous pleural effusion, without radiographic abnormalities in the lungs, constitutes a case of extra-pulmonary TB. A patient with both pulmonary and extra- pulmonary TB should be classified as a case of PTB.
Extra-pulmonary TB (EP TB)
Extra-pulmonary tuberculosis (EPTB) is any bacteriologically confirmed or clinically diagnosed case of TB involving organs other than the lungs such as pleura, lymph nodes (mediastinal, hilar, cervical etc.), larynx, meninges, abdomen, genitourinary tract, spine, bones and joints, skin etc.