8.2 Key Risk factors
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Children infected with M. tuberculosis are not usually ill and do not exhibit symptoms of TB unless the disease is active. Only a small percentage of children who inhale the TB organism develop active disease. Certain groups are at far greater risk than others.
Key risk factors for TB in children
- Household or close contacts of a smear positive or culture positive pulmonary TB (parents, siblings, close relatives, caregivers, neighbors and teachers)
- Age <5 years: The risk of developing TB disease is highest in very young children, who are immune immature
- Severe malnutrition or other Immunosuppressive conditions
- Measles in the previous 3 months
- Whooping cough
- HIV infection
- Being on steroids or other immunosuppressive drugs
- The time since exposure or infection: the vast majority of children who develop TB disease do so within the first year of exposure to and infection with M. tuberculosis.
Other high risk factors are HIV/AIDS, diabetes, end-stage renal failure, cancer, connective tissue disease, silicosis, gastrectomy, solid organ transplantation and patients on prolonged steroid. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes patient have the increased risk of having TB
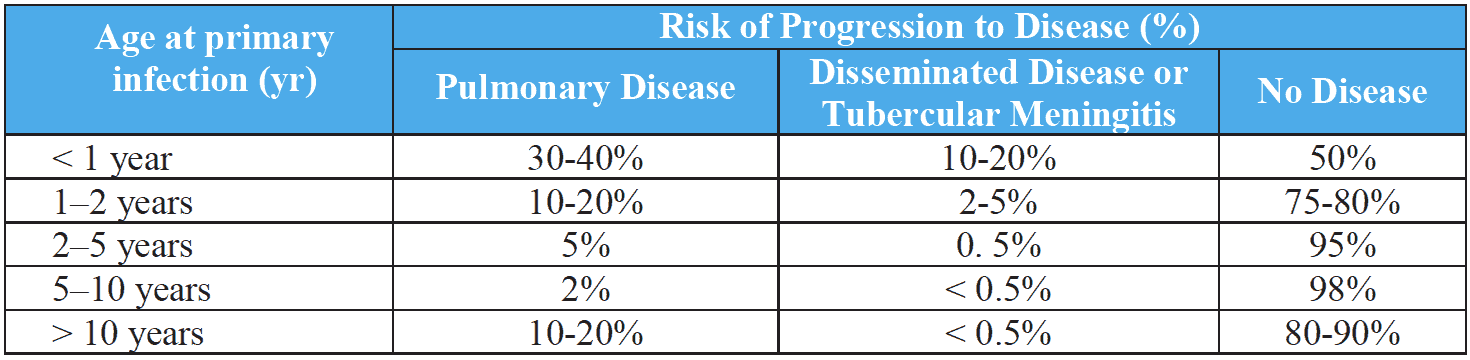
Age-specific risk of progression to disease after primary infection with M. tuberculosis in immunocompetent children